Content Management Systems (CMS): WordPress, Joomla & Drupal - Web Hosting learn
In today's digital world, managing website content efficiently is crucial. Content Management Systems (CMS) have become indispensable tools for creating, managing, and publishing website content without needing deep technical skills. Platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal are leading examples, each offering unique features and catering to different user needs.
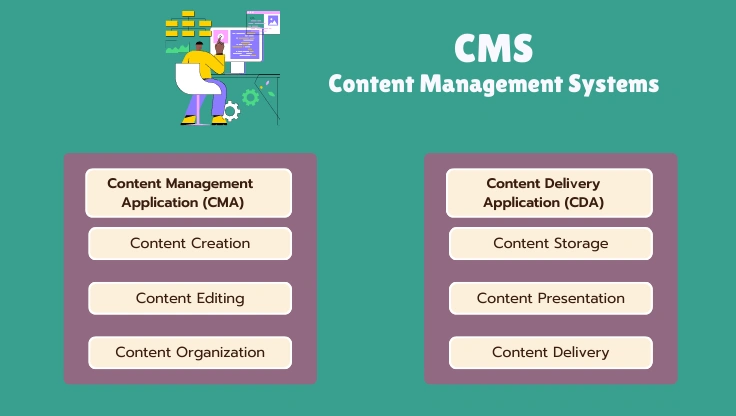
Content Management Systems (CMS) are software applications that allow users to create, manage, and modify content on a website without requiring specialized technical knowledge of coding or web development. A CMS typically consists of two major components: a Content Management Application (CMA) and a Content Delivery Application (CDA).
Let's dive into the world of CMS, exploring what exactly a CMS is, why they are so essential, their key components, and detailed looks at WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal. We will also discuss how to choose the right CMS for your needs and the overall benefits and limitations of using a CMS.
- 1 Understanding Content Management Systems (CMS)
- 2 What is a Content Management System (CMS)?
- 3 Why Use a CMS?
- 4 Key Components of a CMS
- 5 WordPress: User-Friendly CMS
- 6 Joomla: Flexible & Versatile CMS
- 7 Drupal: Powerful & Developer-Focused CMS
- 8 Choosing The Right CMS
- 9 Benefits and Limitations of Using CMS
Content
1. Understanding Content Management Systems (CMS)
1.1. What is a Content Management System (CMS)?
A
Think of a CMS as the control panel for your website's content:
- Word Processor Analogy: Just like you use a word processor (like Microsoft Word or Google Docs) to create and format documents without needing to understand file formats or printing protocols.
- CMS Role: A CMS is like a word processor for your website. It provides tools to write, format, and organize web content (text, images, videos) without needing to code HTML, CSS, or manage databases directly.
A CMS simplifies website management, making it accessible to individuals and organizations without technical teams.
1.2. Why Use a CMS?
Using a CMS offers numerous advantages, making website management more efficient and accessible. Here’s why CMS platforms are so popular:
- User-Friendly Interface: CMS platforms provide intuitive interfaces, often with visual editors, making content creation and editing straightforward for non-technical users.
- Separation of Design and Content: CMS separates website design from content. Designers can focus on creating templates and themes, while content creators can focus on writing and publishing content without altering the design.
- Efficient Content Management: CMS tools offer features for organizing content, managing media files, setting up navigation, and controlling publishing workflows.
- Scalability and Flexibility: CMS platforms can handle websites of all sizes, from small blogs to large, complex websites. They are also flexible and can be extended with plugins, themes, and custom code to add functionality and features.
- SEO Friendly: Most CMS platforms are designed with SEO in mind, offering features and plugins to optimize content for search engines, improving website visibility.
- Collaboration: CMS supports multi-user environments, allowing teams to collaborate on website content with different roles and permissions.
- Pre-built Templates and Themes: CMS platforms offer a wide variety of templates and themes, allowing users to quickly change the design and look of their website without coding.
- Plugins and Extensions: CMS ecosystems include plugins and extensions that add functionality, from contact forms and e-commerce features to SEO tools and social media integration.
In short, CMS platforms empower users to manage websites effectively, efficiently, and without extensive technical skills, making web presence accessible to a broader audience.
1.3. Key Components of a CMS
A typical CMS includes several core components that work together to facilitate content management:
- Content Management Application (CMA): This is the user interface that allows you to add, edit, and remove content from your website. The CMA is where content creators and editors work.
- Visual Editors: WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editors that allow content creation and formatting similar to word processors.
- Content Organization Tools: Features for categorizing, tagging, and structuring content.
- Workflow Management: Tools for managing content creation and publishing processes, including approvals and scheduling.
- User Management: Systems for managing user roles and permissions, controlling access to different parts of the CMS.
- Content Delivery Application (CDA): This is the backend that takes the content entered in the CMA, stores it, and delivers it to website visitors. The CDA handles the technical delivery of content.
- Database Management: Stores and retrieves content, user data, and settings.
- Template Engine: Applies designs (themes or templates) to the content for display.
- API (Application Programming Interface): Allows the CMS to interact with other systems and services.
- SEO and Performance Features: Built-in tools or extensions to optimize website performance and SEO.
- Database: The database is where all the website content, user information, settings, and other data are stored. Common databases used with CMS include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and others.
- Themes/Templates: Themes control the visual design of the website. They define the layout, colors, fonts, and overall style. CMS platforms offer a wide variety of themes, and users can also create or customize their own.
- Plugins/Extensions: Plugins are add-ons that extend the functionality of the CMS. They can add features like contact forms, e-commerce capabilities, SEO tools, social media integration, and much more.
These components together provide a comprehensive platform for managing all aspects of a website's content and presentation.
1.4. WordPress: User-Friendly CMS
Key characteristics of WordPress:
- Ease of Use: WordPress is famous for its user-friendly interface, making it accessible to beginners. Content creation and website management are intuitive.
- Large Community and Support: It has a massive global community, offering extensive support, documentation, and resources. Help is readily available, and there's a wealth of tutorials and guides.
- Extensive Theme and Plugin Ecosystem: WordPress boasts thousands of themes and plugins, both free and premium, allowing users to customize design and add virtually any functionality needed.
- Versatility: While initially for blogging, WordPress is now used for all types of websites – blogs, business sites, e-commerce stores, portfolios, forums, and more.
- SEO Friendly: WordPress is inherently SEO-friendly and offers numerous plugins to further enhance SEO capabilities.
- Scalability: WordPress can scale from small personal blogs to large, high-traffic websites.
- Open Source and Free: WordPress is open-source and free to use, which contributes to its large community and wide adoption.
WordPress is an excellent choice for users who need a balance of ease of use, flexibility, and a wide range of customization options. It's suitable for bloggers, small businesses, and large organizations alike.
1.5. Joomla: Flexible & Versatile CMS
Key characteristics of Joomla:
- Flexibility and Power: Joomla is highly flexible and powerful, suitable for complex websites, applications, and online services. It offers more built-in features than WordPress, especially for complex content types and user management.
- Advanced User Management: Joomla has a robust user management system, making it ideal for websites requiring complex user roles and permissions.
- Multilingual Capabilities: Joomla is well-suited for multilingual websites, with strong built-in support for managing content in multiple languages.
- Developer-Friendly: Joomla is favored by developers for its MVC (Model-View-Controller) framework, making it easier to build custom extensions and complex applications.
- Good for Complex Websites: It's often chosen for e-commerce sites, social networking sites, and other complex web applications.
- Less Theme and Extension Variety Than WordPress: While Joomla has a good selection of extensions and templates, it's not as vast as WordPress's ecosystem.
Joomla is a strong choice for users who need a powerful, flexible CMS with advanced features and are comfortable with a somewhat steeper learning curve than WordPress. It's well-suited for more complex websites and applications.
1.6. Drupal: Powerful & Developer-Focused CMS
Key characteristics of Drupal:
- Highly Flexible and Customizable: Drupal is extremely flexible and customizable, allowing developers to build highly tailored and complex websites and applications.
- Robust and Secure: Known for its robust architecture and strong security features, making it suitable for government, enterprise, and organizations with high-security needs.
- Powerful Core Features: Drupal's core system is very powerful, offering advanced features for content management, user permissions, and data handling.
- Developer-Centric: Drupal is designed with developers in mind, offering a powerful API and modular architecture that is excellent for custom development.
- Taxonomy and Data Handling: Drupal excels in managing complex data structures and taxonomies, making it ideal for websites with large amounts of structured content.
- Steeper Learning Curve: Drupal has a steeper learning curve compared to WordPress and Joomla, especially for non-developers. It requires more technical expertise to set up and manage.
- Smaller Theme and Module Ecosystem: While Drupal has a solid collection of modules and themes, it's smaller compared to WordPress and Joomla.
Drupal is the CMS of choice for developers and organizations that require maximum control, flexibility, and robustness for complex, custom web applications. It's ideal for projects with sophisticated content and functionality needs.
1.7. Choosing The Right CMS
Selecting the right CMS depends on your specific needs, technical skills, and website goals. Here are some considerations to help you choose:
- Ease of Use vs. Flexibility:
- WordPress: Easiest to use, great for beginners, but can be very flexible with plugins and themes.
- Joomla: Balance of ease of use and flexibility, suitable for users with some technical inclination.
- Drupal: Most powerful and flexible, but with a steeper learning curve, best for developers and complex projects.
- Website Type and Complexity:
- Blogs, Small Business Sites, E-commerce (basic): WordPress is often sufficient and easy to set up.
- Complex Websites, E-commerce (advanced), Social Networks, Multilingual Sites: Joomla or Drupal might be more suitable due to their advanced features.
- Highly Custom Web Applications, Enterprise Solutions, Government Websites: Drupal is often preferred for its robustness and customization.
- Technical Skills and Resources:
- Beginners, Non-Technical Users: WordPress is the most accessible.
- Users with Some Technical Skills: Joomla offers a good balance.
- Developers, Technical Teams: Drupal is designed for those with strong technical expertise.
- Community and Support:
- WordPress: Largest community, abundant resources and support.
- Joomla & Drupal: Smaller but still active communities, good documentation and developer resources.
- Scalability Requirements:
- All three CMS platforms (WordPress, Joomla, Drupal) can be scaled: However, Drupal is often favored for very large, high-traffic, and complex websites due to its architecture.
Consider these factors in relation to your project requirements to select the CMS that best aligns with your goals and capabilities.
1.8. Benefits and Limitations of Using CMS
Content Management Systems offer significant advantages but also come with certain limitations:
Benefits:
- Content Creation and Management Efficiency: Simplifies and speeds up content creation, editing, and publishing.
- Non-Technical Accessibility: Allows users without coding skills to manage website content effectively.
- Design Flexibility: Themes and templates allow for easy changes to website design without altering content.
- Extensibility: Plugins and extensions add functionality and features, making CMS adaptable to various needs.
- SEO and Performance Features: Tools and features to optimize websites for search engines and performance.
- Collaboration and Workflow: Supports team-based content creation and publishing workflows.
Limitations:
- Customization Complexity for Advanced Features: While CMS platforms are flexible, highly custom or unique features might still require coding and development expertise.
- Performance Overhead: CMS can sometimes introduce performance overhead compared to static websites or highly optimized custom-coded sites, especially if not properly configured or if too many plugins are used.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Popular CMS platforms can be targets for security vulnerabilities. Regular updates and security practices are essential.
- Learning Curve (Varies by CMS): While generally user-friendly, some CMS platforms, like Drupal, have a steeper learning curve, especially for advanced configurations.
- Maintenance and Updates: CMS platforms, themes, and plugins require regular updates for security and compatibility, which can be an ongoing maintenance task.
Overall, CMS platforms are powerful tools that greatly simplify website content management and creation for a wide range of users and website types. However, understanding their limitations and choosing the right CMS for your needs is crucial for success.
9. Comparing CMS Platforms: WordPress, Joomla, Drupal
Want to Learn More Web Hosting Stuff? learn's This Way
Find Recommended Web Hosting Providers
FAQ About Content Management Systems (CMS)
What is a Content Management System (CMS)?
A Content Management System (CMS) is a software application that allows users to create, manage, and modify content on a website without needing to write code.
What are the benefits of using a CMS?
CMS benefits include ease of use, efficient content management, separation of design and content, scalability, SEO-friendliness, and availability of themes and plugins.
What are the key components of a CMS?
Key components include a Content Management Application (CMA) for content creation, a Content Delivery Application (CDA) for content delivery, a database for storage, themes for design, and plugins for added functionality.
What is WordPress?
WordPress is the most popular CMS, known for its user-friendliness, vast ecosystem of themes and plugins, and versatility for various website types from blogs to e-commerce sites.
What is Joomla?
Joomla is a flexible and powerful CMS, favored for complex websites and applications, offering advanced user management and multilingual capabilities. It's more developer-friendly than WordPress.
What is Drupal?
Drupal is a highly robust and customizable CMS, known for its security and power. It is developer-centric and best suited for complex, custom web applications and websites with sophisticated needs.
Which CMS is easiest to use: WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal?
WordPress is generally considered the easiest to use, especially for beginners. Joomla is moderately easy, while Drupal has a steeper learning curve and is more developer-focused.
Can I build an e-commerce website with a CMS?
Yes, all three CMS platforms (WordPress, Joomla, Drupal) can be used for e-commerce. WordPress with WooCommerce, Joomla with VirtueMart or other extensions, and Drupal with Drupal Commerce are all viable options.
Do I need coding skills to use a CMS?
No, you generally do not need coding skills to use a CMS for basic content management. However, for advanced customization, theme modifications, or plugin development, coding knowledge can be beneficial, especially with Joomla and Drupal.
Are CMS platforms SEO-friendly?
Yes, most CMS platforms are designed to be SEO-friendly, offering features and plugins to optimize content for search engines. WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal all have SEO capabilities and extensions.